International Journal of Preclinical and Clinical Research
Year: 2021, Volume: 2, Issue: 4, Pages: 87-92
Original Article
Deepa Patil 1, Mohan Kumar✉ 1, G M Megha 2, Shreekrishna 3
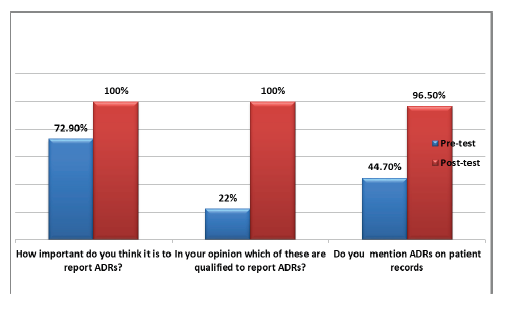
Objectives: To assess the Knowledge, Attitude and Practices of nursing students on monitoring and reporting of adverse drug reactions in a tertiary care hospital. Methodology: This questionnaire based study was conducted in a tertiary care hospital on 85 Prefinal and final year nursing students. The study instrument was a pre designed questionnaire which included the Knowledge of the ADRs reporting, the attitudes towards the reporting, and the factors which could hinder the reporting. The students were given an educative and interactive session for clearance of their understanding about Pharmacovigilance. The post-session questionnaire was also completed to assess their understanding. Results: A total of 85 students participated. The median knowledge, attitude scores before the intervention were 42.5%, 46.6% respectively. After the intervention the scores increased significantly to 89.4%, 98.8% respectively.
Keywords: Adverse Drug Reactions, Pharmacovigilance, Questionnaire, Knowledge Attitude and Practices, Nursing students
© 2021 Patil et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Published By Basaveshwara Medical College & Hospital, Chitradurga, Karnataka.
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.