International Journal of Preclinical and Clinical Research
Year: 2020, Volume: 1, Issue: 1, Pages: 7-11
Original Article
L J Kiran1, B E Pradeep2, M S Raghuprasada3, V S Harish Kumar3, A N Pradeep4, K G Shivashankaramurthy5*
1 Professor and Head, Department of Pharmacology, S.S Institute of Medical Sciences and Research Centre, Davangere, Karnataka
2 Tutor, Department of Pharmacology, S.S Institute of Medical Sciences and Research Centre, Davangere, Karnataka
3 Associate Professor, Department of Pharmacology, S.S Institute of Medical Sciences and Research Centre, Davangere, Karnataka
4 Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacology, S.S Institute of Medical Sciences and Research Centre, Davangere, Karnataka
5 Professor, Department of Pharmacology, S.S Institute of Medical Sciences and Research Centre, Davangere, Karnataka
*Corresponding author
Email: [email protected]
Received Date:04 December 2020, Accepted Date:12 December 2020, Published Date:21 December 2020
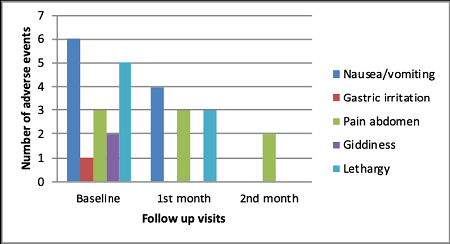
Iron deficiency anaemia (IDA), the most prevalent nutritional deficiency leading to mortality globally. Oral ferrous salts are effectively used to treat iron deficiency in pregnancy. For the present study, no direct comparison demonstrating the efficacy of ferrous ascorbate and ferrous calcium citrate was considered. An open-label, observational study was designed and conducted for two months. Subjects were randomly allocated to two groups (Group A and Group B). The medication followed in Group A was, ferrous calcium citrate with elemental iron 50 mg; In Group B ferrous ascorbate containing elemental iron 100 mg orally for two months at bedtime. Haemoglobin levels, other hematological parameters, weight changes, side effects, conjunctival colour and general wellbeing were assessed in every visit (i.e. 0, 30th and 60th day) for clinical efficacy assessment. There was an increase in the mean serum haemoglobin and ferritin levels (p<0.05). In Group A and Group B, the mean values of all the assessment parameters increased significantly (p<0.05) in follow-up visits (i.e. 1st month and 2nd month) when compared to baseline values. Out of 69 adverse drug events, 29 (42%) were reported from Group A and 40 (58%) from Group B. Ferrous calcium citrate showed considerable efficacy and safety profiles.
Keywords: Iron deficiency; anaemia; haemoglobin; ferrous calcium citrate; ferrous ascorbate
© 2020 Kiran et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Published By Basaveshwara Medical College & Hospital, Chitradurga, Karnataka.
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.