International Journal of Preclinical and Clinical Research
DOI: 10.51131/IJPCCR/v3i2.22_28
Year: 2022, Volume: 3, Issue: 2, Pages: 37-44
Original Article
G Prashanth 1 , Md. Murtuza Kauser 2 , Basavaraj Savadi 3 , B M Rashmi ✉ 4
Received Date:02 May 2022, Accepted Date:06 June 2022, Published Date:05 July 2022
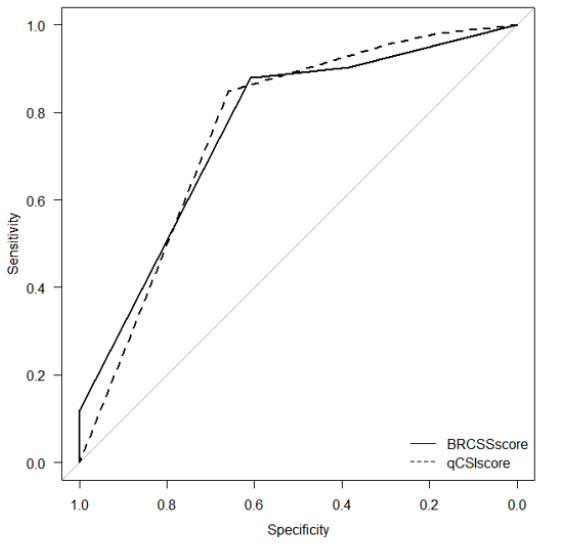
The usefulness of risk screening tools in triaging and predicting likelihood of adverse outcomes of COVID-19 patients at first point of contact, would prevent overestimation or underestimation of severity risk in COVID pneumonia. BCRSS algorithm, a dynamic risk predictor, that uses clinical parameters of patient to assess need for escalating levels of respiratory support(Non-invasive ventilation, intubation, proning) to suggest treatment recommendations. Quick COVID-19 Severity Index (qCSI) is based on 3 variables (nasal cannula flow rate, respiratory rate, minimum documented pulse oximetry). To compare prognostic performance of BCRSS and qCSI-scores of hospitalized patients diagnosed with COVID-19. This is a Retrospective record-based study conducted at a tertiary hospital in Karnataka among COVID-19 patients. Patient’s clinical severity grade classification was done according to standard guidelines by Government of India. BCRSS and qCSI scores were calculated using baseline clinical information of patients. Statistical analysis used were Chi-squared test, regression analysis and ROC curve. The study results showed that out of 363 patients, majority of patients with high qCSI risk score of 3 and those with high BCRSS risk score of 4 were found to have high rates of ICU admissions and in-hospital deaths (66.9% and 44.4% for qCSI-3; 34.6% and 1.9% for BCRSS-4). With every unit increase in qCSI and BCRSS scores, there were 2.68 and 1.58 times more risk of fatality respectively. ROC curves for qCSI and BCRSS scales showed high area under curve:qCSI(AUC:0.761) and BCRSS(AUC:0.760), to predict in-hospital fatality. The study has shown that both qCSI and BCRSS scoring models have good results for predicting probabilities of ICU admissions and in-hospital mortality of COVID-19 patients.
Key Messages: These risk prediction models, if applied during the initial clinical assessment stage, could help in better triaging, risk prediction, better treatment of COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: Quick COVID-19 Severity Index, Brescia-COVID Respiratory Severity Scale, in-hospital mortality, COVID-19, ICU admission
© 2022 Prashanth et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Published By Basaveshwara Medical College & Hospital, Chitradurga, Karnataka.
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.