International Journal of Preclinical and Clinical Research
Year: 2021, Volume: 2, Issue: 2, Pages: 38-41
Original Article
N Thweja 1, D Divya 2,*, Vickram 3
Received Date:07 July 2021, Accepted Date:12 July 2021, Published Date:19 July 2021
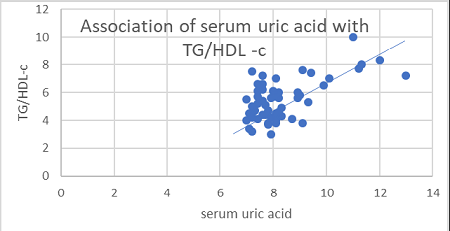
Insulin resistance (IR) is the principle etiological factor for development and progression of type-2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and decreased insulin function. Independently, increased serum uric acid (SUA) is known to play a critical role in the development of T2DM as well as in progression of its complications. To assess the correlation between SUA levels and IR in diabetic patients, data with lab investigations of HbA1c, fasting levels of serum glucose, UA, TAG, HDL-C of confirmed and known cases of T2DM were collected from the Hospital Biochemistry Laboratory, DMWIMS Hospital, Wayanad, Kerala. Fasting ratio of TAG to HDL-C was used as an index for IR. A significant increase in fasting serum glucose, SUA, HBA1C, TAG, TAG/HDL-C ratio (IR) and a significant decrease in HDL-C were observed in data of cases when compared with the data of normal healthy subjects. This study shows a positive correlation between SUA levels and IR in known cases of T2DM.
Keywords
type2 diabetes mellitus, serum uric acid, insulin resistance
© 2021 Thweja et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Published By Basaveshwara Medical College & Hospital, Chitradurga, Karnataka.
Subscribe now for latest articles and news.